OSTrails Interoperability Webinar Series: Making Research Tools EOSC-Ready Through Common Standards

Over the past semester, OSTrails launched the first part of its Interoperability Webinar Series spotlighting the development of Interoperability Frameworks (IFs) under the OSTrails Reference Architecture.
Key takeaways
- Early access to FAIR-IF, DMP-IF, and SKG-IF specifications to prepare tools and workflows for integration.
- Practical examples of embedding frameworks into widely used platforms for EOSC alignment.
- Networking with EOSC, RDA, and related initiatives to align with interoperability standards.
- Exchange of insights on APIs, benchmarks, and extension mechanisms for real-world application.
- Direct input into framework development through use cases and feedback.
Nearly 300 participants joined the sessions on the Assessment-IF (previously FAIR‑IF), the Data Management Plan IF (DMP-IF), and the Scientific Knowledge Graphs IF (SKG-IF), representing a diverse mix of data stewards, librarians, repository managers, software developers, researchers, and open science coordinators from universities, research infrastructures, and international organisations. They came to learn how these efforts are enabling seamless collaboration and information exchange across research data management (RDM) tools and communities.
Main message.
In the context of the Open Science agenda, interoperability of research practices, tools, and infrastructures is no longer optional. It is essential for research to function at a scale across domains and communities. Achieving this, however, requires more than technical fixes — it demands alignment, shared standards, and collective effort.
OSTrails is working with the community to align practices, clarify responsibilities, and define common interfaces between tools and services. The immediate goal is technical compatibility, ultimately supporting a research ecosystem where infrastructures can interact by design, policies are easier to implement, and knowledge flows more openly across systems.
Session Highlights
Assessments IF (previously FAIR-IF): Mark Wilkinson (UPM), WP3 lead (Assessment tools & services), introduced the Assessment-IF, developed to address the lack of harmonisation across assessment tools and the inconsistent interpretation of FAIR principles. The framework supports interoperability and is designed to be embedded in DMP platforms to provide real-time, standardised feedback.
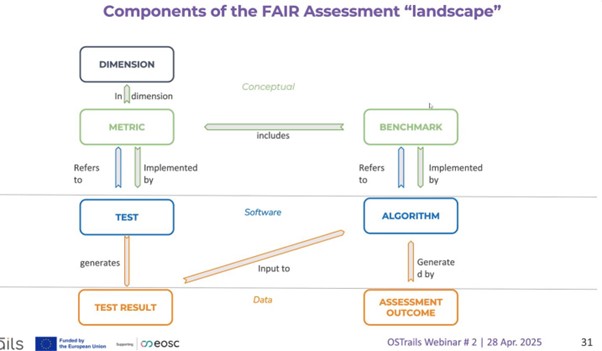 Components of the FAIR Assessment landscape, as presented during the webinar.
Components of the FAIR Assessment landscape, as presented during the webinar.
“We want to design and publish metrics and tests for a wider range of digital objects beyond data and including domain specific assessments.”
- Mark Wilkinson
In the discussion, participants showed strong interest in the upcoming API specifications that will enable tools to interact and harmonise outputs, as well as in approaches for describing algorithms as community judgments over benchmarks. There was also significant engagement around governance models involving diverse stakeholders — including domain experts, coders, and FAIR specialists — in the validation of metrics and tests.
DMP-IF: Marek Suchánek (CTU), WP2 (Plan-Track-Assess Alignment Implementation) lead, presented DMP-IF as a solution to fragmentation and lack of machine-actionability in current data management plans. Building on the RDA DMP Common Standard, the framework adds an application profile and a common API. This enables platforms to integrate with FAIR assessment tools, repositories, and SKGs in a uniform way while adapting the standard to European research needs. In doing so, it supports policy compliance and accommodates diverse research outputs.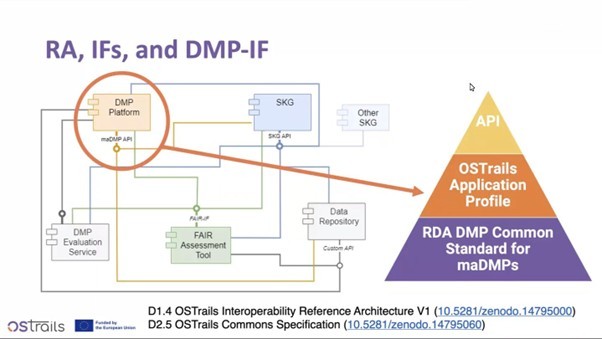 Insights on DMP-IF presentation.
Insights on DMP-IF presentation.
“We are building on top of the DMP Common Standard from RDA by creating an application profile and API specification for DMP platforms, enabling interoperability, extensibility, and alignment with real-world needs such as policy compliance and support for diverse research outputs.”
- Marek Suchánek
During the discussion, participants highlighted how the framework can connect data repositories and DMP platforms in both directions — either fetching DMPs or pushing updates, such as dataset publication events, via the planned API. They emphasised its tool-agnostic design and its potential to reduce duplication through automation, ensure policy compliance, and support diverse outputs, including software management plans. Questions also covered reusing example DMPs, integrating with OSTrails DMP platforms and ensuring compatibility across systems.
SKG-IF: Andrea Mannocci (CNR), co-chair of the SKG-IF RDA WG, introduced the framework and its role in enabling cross-disciplinary research through semantic and technical interoperability. Building on the RDA model, SKG-IF provides a common data model, API specifications, and an extension mechanism to align and integrate knowledge graphs across systems, addressing the fragmentation caused by isolated, non-aligned graphs.
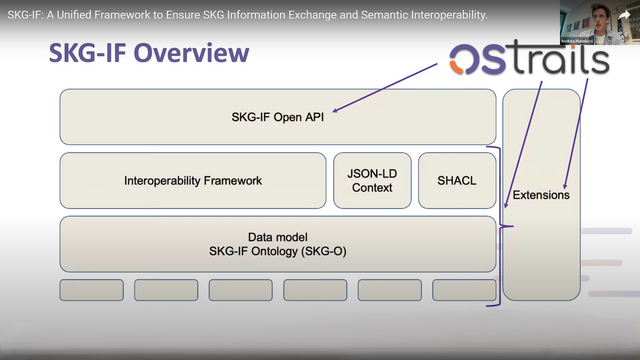 Overview of OSTrails contribution to the SKG-IF core model.
Overview of OSTrails contribution to the SKG-IF core model.
“The SKG-IF isn’t magic. There’s no central implementation or governing body that operates a service or infrastructure to enable dialogue between different SKGs. That might sound reductive, but in essence, SKG-IF is a set of guidelines. Anyone who wants their SKG to be interoperable with others and compliant with SKG-IF must follow these guidelines.”
- Andrea Mannocci
In the discussion, participants explored how communities — both established and emerging — can contribute requirements to SKG-IF extensions, either through the RDA Working Group or dedicated extension projects. Questions focused on the level of technical expertise needed to develop extensions and the importance of practical guidance and real-world examples. Interest also centred on keeping the extension process accessible to non-experts, providing templates, and maintaining strong links between community-driven extensions and the core model.
Why was it important for OSTrails?
The webinar series provided OSTrails with a high-impact opportunity to present its core technical developments and engage with the research community and EOSC landscape. The events helped validate the project’s direction, and practical feedback surfaced for several topics, ranging from inconsistencies in FAIR metrics to technical needs for DMP platform integration and SKG alignment. These insights are now shaping the ongoing refinement of each of the three frameworks to better support real-world use cases.
Why was it important for the Research Community in general?
The series enabled the research community to engage directly with the emerging frameworks and provide input early in their development. It also fostered alignment with ongoing international and EOSC-related initiatives, such as the RDA DMP Common Standard and SKG-IF Working Group and FAIR Metrics and Digital Objects Task Force, and complementary projects like FAIRCORE4EOSC and FAIR-IMPACT. These connections ensure that OSTrails developments build on widely adopted standards, support machine-actionable outputs, enable integration with established platforms, and address shared priorities such as policy compliance, persistent identifiers, and cross-platform interoperability.
Conclusions
The OSTrails webinars highlighted a shared need across the research landscape for more aligned, automated, and interoperable infrastructures. Each framework is helping to bridge gaps, whether in FAIR evaluation, data management automation, or SKG integration, and their development is being guided by community input. As they evolve, the IFs are poised to support a more open, trustworthy, and connected research ecosystem.
Further Resources
Explore the full webinar series and access resources (recordings and slides) here.
Discover the documentation for the OSTrails Interoperability Architecture and its three Interoperability Frameworks here.



